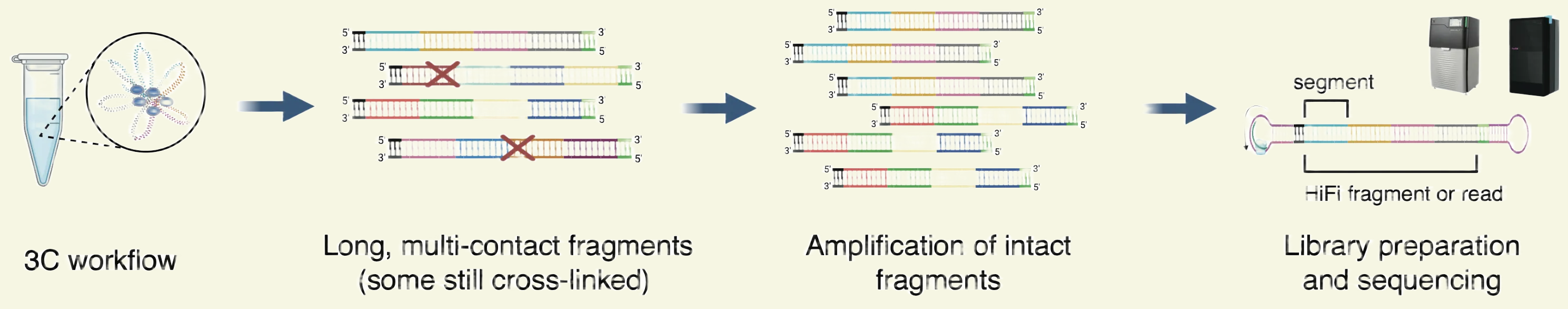
Step 1: CiFi starts with an in situ 3C/Hi-C-style proximity ligation: chromatin is cross-linked, cut with a restriction enzyme, and nearby DNA fragments are ligated together, then crosslinks are reversed and DNA is purified.
Step 2: CiFi boosts yield from low input by adding a high-fidelity, genome-wide amplification step and preparing a PacBio SMRTbell library for HiFi sequencing (with size selection), enabling long multi-contact reads from as little as ~60,000 cells.
Step 3: The long HiFi concatemers are split in silico at restriction sites into multiple interacting segments, which are converted into chromatin contacts for downstream 3D genome analyses.